SnapStream servers are equipped with dual hot-swap power supplies that are both redundant, and load-balancing. A single unit may be replaced without a system power-down. The servers also support auto detection of 100-240V and 50-60Hz power.
Below are the server configurations and their respective power consumption statistics.
| Storage Level | Chassis Size | Total Number of Drives | Power Supply Used | Idle Draw Watts | Idle Draw Amps | Max Draw Watts | Max Draw Amps | Power Off Draw |
| 3 TB | 3U | 7 | Dual 800 Watts | 190 | 1.6 | 240 | 2.0 | 30 W |
| 6 TB | 3U | 11 | Dual 800 Watts | 250 | 2.1 | 300 | 2.5 | 30 W |
| 9 TB | 3U | 16 | Dual 800 Watts | 325 | 2.7 | 375 | 3.1 | 30 W |
| 12 TB | 4U | 20 | Dual 900 Watts | 385 | 3.2 | 435 | 3.6 | 30 W |
| 15 TB | 4U | 24 | Dual 900 Watts | 445 | 3.7 | 495 | 4.1 | 30 W |
Connecting Power - Best Practices
Minimal Configuration

In this configuration. each of the system's power supply units are plugged into a a single ‘uninterrupted power supply’ (UPS). This configuration provides protection against a single system power supply unit failure and momentary power outages or failures. This configuration is vulnerable against extended power failures due to the single power source. This configuration is also vulnerable to UPS failures as both power supply units connect to the same UPS.
Better Configuration
 In this configuration, each of the system's power supply units are plugged into a separate UPS. This configuration provides for protection against single system power supply unit failure. The system is also better protected against power outages since the amount of backup power is effectively doubled. The vulnerability against a single UPS failure has been eliminated as well.
In this configuration, each of the system's power supply units are plugged into a separate UPS. This configuration provides for protection against single system power supply unit failure. The system is also better protected against power outages since the amount of backup power is effectively doubled. The vulnerability against a single UPS failure has been eliminated as well.
Best Configuration
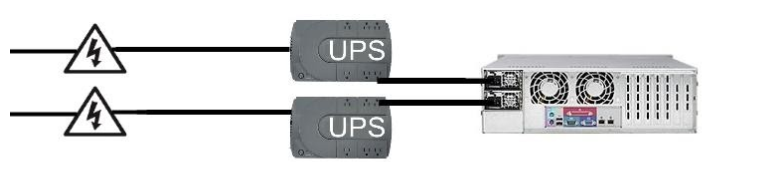 In this configuration, each of the system's power supply units are plugged into its own UPS and each UPS is powered by separate and independent circuits. This provides the best protection against a single power supply failure, single UPS failure, and a single or double power circuit failures.
In this configuration, each of the system's power supply units are plugged into its own UPS and each UPS is powered by separate and independent circuits. This provides the best protection against a single power supply failure, single UPS failure, and a single or double power circuit failures.
UPS VA Recommendations
When deciding on UPS hardware, it is important to choose a solution with the appropriate VA rating. This rating allows you to calculate the prospective uptime of a server in the event of a power failure, based on the power draw of the system. Listed below are some approximate times for our servers based on UPS hardware with standard VA ratings.
 | The following calculations are a conservative estimate based on maximum power draw with a full CPU load. |
Single UPS Configuration
| Storage Level | Idle Draw Watts | Max Draw Watts | 500VA | 800VA | 900VA | 1200VA | 1500VA |
| 3 TB | 190 | 240 | 3 min | 15 min | 15 min | 15 min | 20 min |
| 6 TB | 250 | 300 | 3 min | 15 min | 15 min | 15 min | 20 min |
| 9 TB | 325 | 375 | N/A | 10 min | 10 min | 10 min | 13 min |
| 12 TB | 385 | 435 | N/A | 6 min | 6 min | 6 min | 9 min |
| 15 TB | 445 | 495 | N/A | 6 min | 6 min | 6 min | 9 min |
Dual UPS Configuration
| Storage Level | Idle Draw Watts | Max Draw Watts | 500VA | 800VA | 900VA | 1200VA | 1500VA |
| 3 TB | 190 | 240 | 9 min | 25 min | 27 min | 33 min | 38 min |
| 6 TB | 250 | 300 | 9 min | 25 min | 27 min | 33 min | 38 min |
| 9 TB | 325 | 375 | 9 min | 25 min | 27 min | 33 min | 38 min |
| 12 TB | 385 | 435 | 3 min | 15 min | 15 min | 22 min | 24 min |
| 15 TB | 445 | 495 | 3 min | 15 min | 15 min | 22 min | 24 min |
